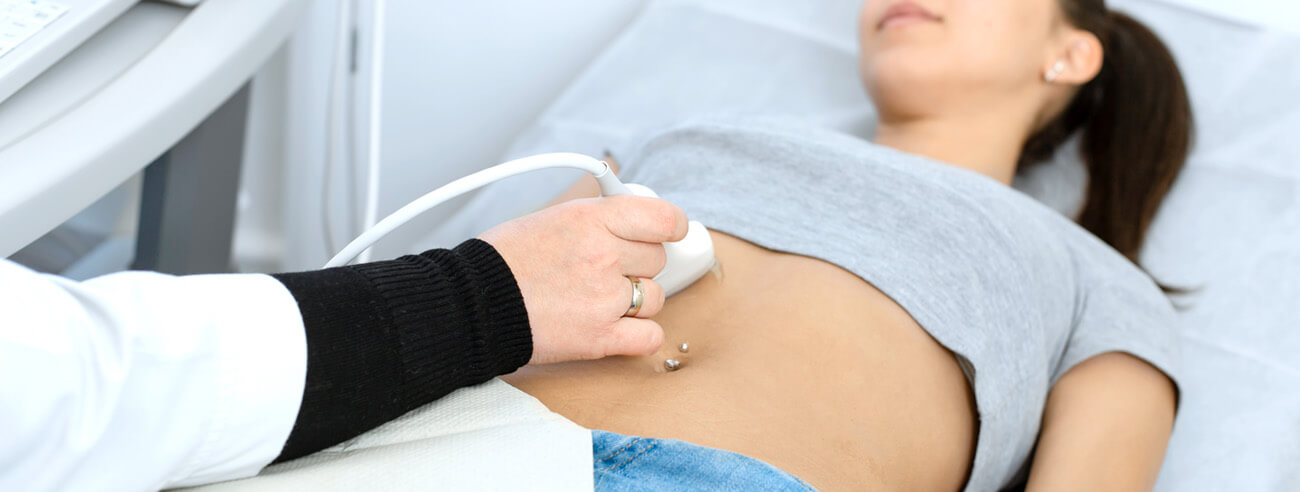
Abdominal Aorta Ultrasound
An Abdominal Aorta Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to evaluate the abdominal aorta, the largest artery in the body. The abdominal aorta supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs.
Purpose of an Abdominal Aorta Ultrasound:
- Screen for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA): An aneurysm occurs when the walls of the aorta weaken, causing it to bulge or dilate. If left untreated, it could rupture and lead to life-threatening bleeding.
- Monitor Known Aneurysms: To assess the sizeand growth of an existing aneurysm.
- Evaluate Symptoms: Sudden abdominal , back, or flank pain may indicate an aorta aneurysm.
- Assess Aortic Health: Identify blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities in eh abdominal aorta.
- Check Blood Flow: Evaluate conditions like aortic dissection or blood clots.
Indications for the Test:
- Risk factors for (AAA), such as: Smoking, High Blood Pressure, High Cholestero, or a family history of aneurysms.
- Symptoms like unexplained abdominal pain, back pain, or a pulsating mass in the abdomen.
- Screening needs based on guidelines (e.g., men aged 60-70 who have smoked).
Procedure:
The patient may either lie down or stand, depending on the area being examined. A water-based gel is applied to the skin to enhance the transmission of sound waves and ensure clear imaging. The ultrasound probe is then moved along the veins, and compression maneuvers are used to assess the collapsibility of the veins and gather information about blood flow. This helps evaluate conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or venous insufficiency. The procedure is non-invasive and painless, with the entire process typically taking 30-45 minutes to complete. The images and data collected during the exam are crucial for diagnosing any vascular abnormalities or blood flow issues.
Results:
Preparation for the test may involve fasting for 6-8 hours prior to the procedure to reduce gas in the intestines, as gas can interfere with the clarity of the ultrasound images. During the test, the patient lies on their back on an examination table, and a water-based gel is applied to the abdomen to enhance the transmission of sound waves. An ultrasound probe is then moved over the abdomen to capture detailed images of the aorta and its branches, helping to assess the condition of the blood vessels. The procedure is non-invasive, painless, and typically takes between 15 to 30 minutes to complete, providing valuable information for diagnosing conditions such as aneurysms or blockages in the aorta.