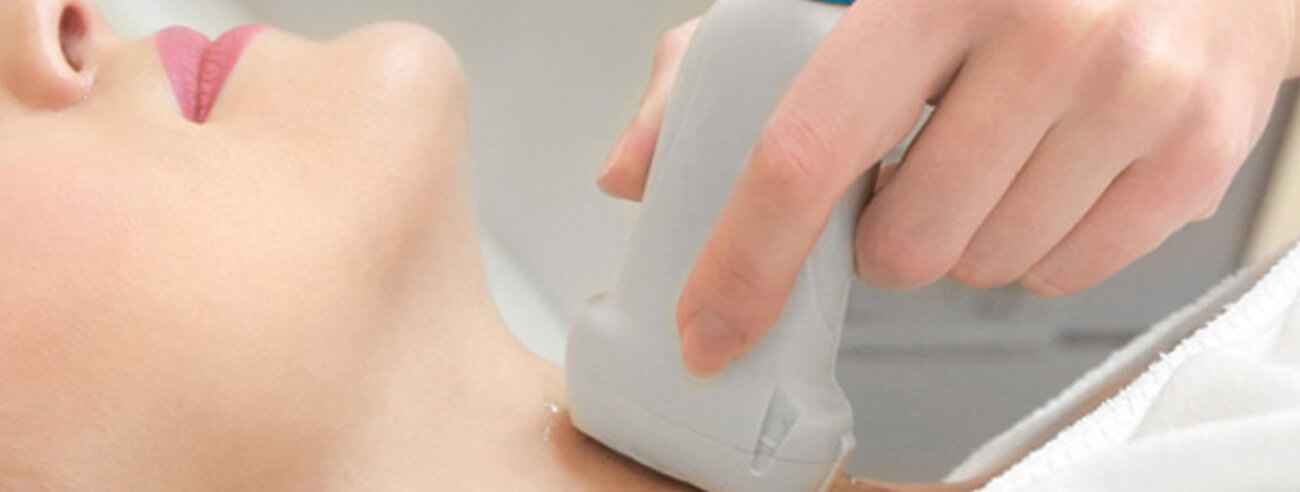
Carotid Duplex
A Coratid Duplex is a non-invasive ultrasound test that combines traditional ultrasound imaging with Doppler ultrasound to evaluate the carotid arteries in the neck. These arteries are critical as they supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. The test is used to detect conditions such as carotid artery stenosis, plaque buildup and other abnormalities that could increase the risk of stroke.
Purpose of a Carotid Duplex:
- To access the risk of stroke.
- To evaluate symptoms such as dizziness, sudden weakness, or vision problems.
- To monitor known carotid artery disease.
- To check for blood flow issues after surgery or stenting.
Indications for the Test:
- Stroke or TIA Symptoms: Sudden weakness, numbness, vision loss, or speech difficulties.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Diagnosing or monitoring stenosis or after surgery/stenting.
- Risk Factors: Hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, or family history of atherosclerosis.
- Bruit: Abnormal sound over the carotid artery.
- Preoperative Assessment: Before cardiovascular or thoracic surgery.
- Follow-up: Monitoring plaque progression or vascular abnormalities.
Procedure:
The patient lies comfortably on the examination table as a clear gel is applied to the neck, helping to facilitate the transmission of sound waves. An ultrasound probe is gently moved over the sides of the neck to capture detailed images and assess blood flow. The procedure is non-invasive and generally takes between 30 to 60 minutes to complete, with no discomfort or pain involved. The gel helps to create a smooth surface for the probe, ensuring accurate readings throughout the process.
Results:
The results of the ultrasound will reveal the condition of the carotid arteries, indicating whether they are normal, partially blocked, or significantly narrowed. If significant narrowing or blockages are detected, it may signal an increased risk of stroke or other vascular issues. In such cases, further evaluation and treatment options, such as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgical intervention, may be recommended to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. The healthcare provider will discuss the findings and determine the most appropriate course of action based on the severity of the blockage.