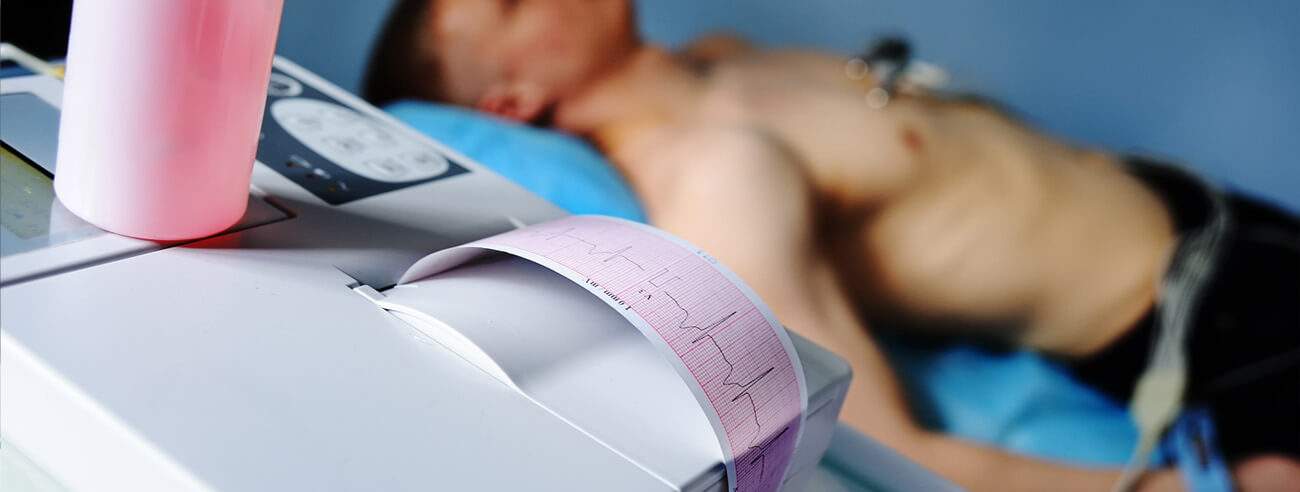
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It produces a visual graph that helps healthcare providers evaluate the heart's rhythm, electrical conduction, and overall function. It is non-invasive, painless, and commonly used to diagnose and monitor heart conditions.
Purpose of an Electrocardiogram:
- Detect abmormalities in heart rhythm.
- Identify signs of inadequate blood flow to the heart muscle.
- To diagnose a heart attack or previous heart damage.
- Monitor changes in heart conditions over time.
- Evaluate the effects of medications or devices likepacemakers.
- Check for electrolyte imbalances affecting the heart.
Indications for the Test:
- Symtoms of Heart Problems: Chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat or palpitations or dizziness or fainting.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment or medications, checking the function of a pacemaker or evaluating the heart before and after surgical procedures.
- Routine screening for individuals with a family history of heart disease or as part of a physical exam in certain populations such as athletes or military personnel.
Procedure:
The patient lies comfortably on an examination table while a healthcare professional attaches electrodes to the chest, arms, and legs using adhesive pads. To ensure optimal contact and accurate readings, the skin may be cleaned or shaved beforehand. These electrodes serve as sensors, detecting the heart's electrical impulses, which are then transmitted to an electrocardiogram (EKG) machine. The machine records these impulses as a series of waves displayed on graph paper or a digital screen, providing valuable insights into the heart's rhythm, rate, and overall electrical activity. The test is quick, non-invasive, and typically lasts about 5 to 10 minutes. Once completed, the results are carefully reviewed and interpreted by a healthcare provider to assess the heart's condition and guide any necessary treatment or further evaluation.
Results:
Normal electrocardiogram (EKG) results display a regular heart rhythm, a normal heart rate, and consistent, well-defined wave patterns, indicating that the heart's electrical activity is functioning properly. Each segment of the EKG tracing follows a predictable pattern, reflecting the coordinated contraction and relaxation of the heart's chambers. In contrast, abnormal results may reveal arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats, signs of a previous or ongoing heart attack, structural abnormalities such as enlarged heart chambers, or electrolyte imbalances affecting heart function. These irregularities provide critical information to healthcare providers, helping them diagnose underlying conditions and determine the appropriate course of treatment or further testing.